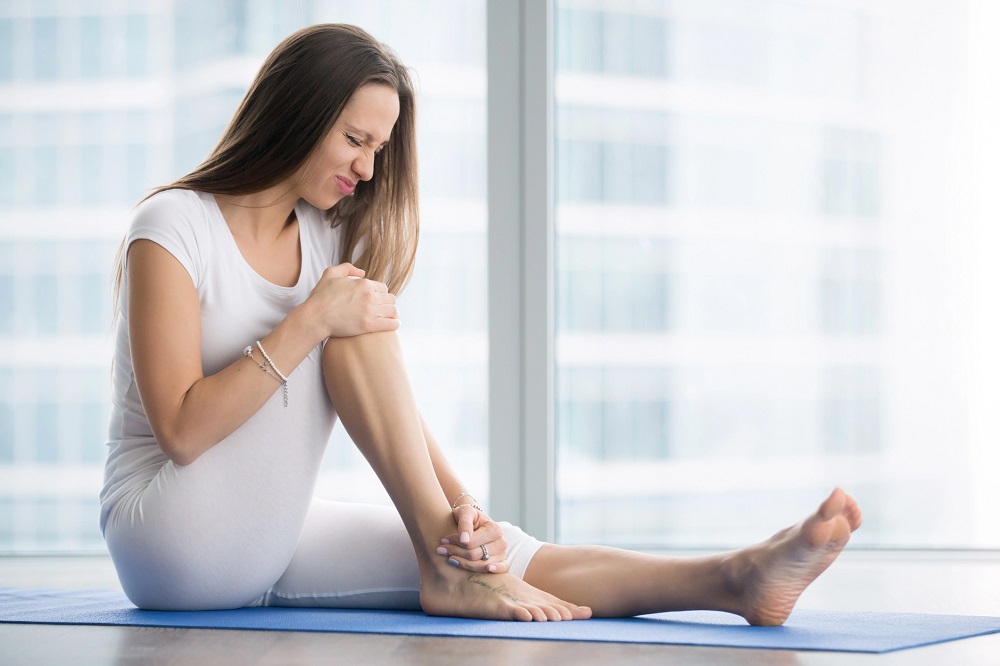
Knee instability is a problem that a lot of us experience every day. Knee instability is most often caused by injuries, congenital disabilities, and illnesses. Knee instability can manifest as knee pain, cartilage damage, knee ligament damage, knee spurs, and abnormal knee motion.
Although many of us know what knee instability is, and some know what causes it, we also know some of the most common causes of knee instability and remedies that can help.
If you want to understand what we mean, read more (อ่านต่อ, which is the term in Thai) to get an idea.
When Is It Caused?
Knee instability can be a chronic injury if left untreated. It is most commonly a result of the knee joints moving into abnormal positions and not being kept stable with proper support. Knee instability can manifest in pain or swelling and can be acute or chronic.
Who Is More Likely To Be Affected By Knee Instability?
The following are more prone to knee instability issues.
- Young athletes who are fit, active, and in their teens and twenties
- Overweight people
- Women who suffer from knee instability are twice as high as the number of men who experience symptoms. Factors associated include age, family history, hormonal imbalance, muscle weakness.
- Gradual wear and tear of the cartilage of the knee
- People with prior injury history
Causes Of Knee Instability
These are the most common causes of knee instability.
Ligament Tears:
Ligament tears can occur either from repetitive or sudden forces to the knee. Instability of the knee can be due to joint damage and muscle imbalance.
Ligament Sprain:
A ligament sprain is the most common cause of knee injury among athletes. The ligaments hold a knee joint together. A sprain of the ligaments allows the tibia and femur to move too far, causing an imbalance in the knee.
Rare Or Unusual Causes Of Knee Instability
Knee instability can also result from the following less common causes.
- Partial Dislocation: An injury that damages both the ligaments and cartilage around the knee bone may result in partial dislocation.
- Tissue Tear: Tissue tears can occur under the kneecap, where the ends of the upper and lower leg bones meet. These injuries often accompany ligament sprains.
- Cartilage Wear: The cartilage in between the bones may wear away over time, causing pain and difficulty moving.
- Birth Deformity: You might be born with a joint structure that makes it easy for the knee to slip out of place.
Meniscal Injury
A meniscus injury is a condition in which the meniscus, cartilage that is part of the knee joint, is torn, injured, or degenerated. Often, the cause is an injury to the knee itself. A meniscus injury is most common in athletes, especially football players involved in certain types of contact, such as tackles and sacks.
Most meniscal injuries are not severe and are treatable conservatively. However, surgical treatment is necessary if symptoms worsen or don’t improve after a few weeks.
Symptoms
Pain is the first and most common symptom, and it can range from a dull ache to a sharp ache. It can also result from knee stiffness or a swollen knee.
ACL Injury
An ACL injury is one of the most common injuries that the human body encounters. It is an injury that frequently occurs in active sports, such as sports like football and basketball. The main symptom of this injury is pain in the knee and a lack of stability.
Knee (MCL) Sprain
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of the six important ligaments that connect the shin bone (tibia) and thigh bone (femur). The MCL connects the shin bone and the thigh bone and helps keep the knee stable during the leg movement. An MCL sprain is generally caused during high-impact activities due to a blow to the knee or a fall.
Knee Instability Treatments At Home
- Rest- Do not continues to move if you have pain in and around the knee. It’s a good idea to take some rest.
- Over-The-Counter Medicines – Most people can handle knee pain, but it is sometimes necessary to treat it with ibuprofen.
When To See A Doctor
The knee joint is a complicated and relatively inaccessible place. Even a relatively minor injury can be tricky to diagnose. If your pain is getting worse, or if you are also experiencing any of the following, you should consult a physician: swelling, stiffness, and swelling that doesn’t go away; loss of function, such as being unable to lift
Knee pain can be a symptom of a more severe problem like cartilage loss, a knee injury, or a fracture. A doctor can examine you for any signs of injury or infection.